Digestive issues can sometimes be caused by unexpected factors, and one condition that often flies under the radar is a bile duct obstruction. It’s a health issue that can lead to a wide range of digestive problems, and if left untreated, may lead to more severe complications. If you’ve experienced digestive discomfort, jaundice, or noticed changes in your stools, it might be a sign that something’s going on with your bile duct.
In this article, we’ll explore what bile duct obstructions are, how they impact digestion, and why it’s crucial to address them early on.
What Is a Bile Duct Obstruction?
The bile duct is a small but essential tube that transports bile from your liver and gallbladder into the small intestine. Bile is a digestive fluid that helps break down fats in the food you eat. When the bile duct becomes blocked, it’s like hitting a roadblock in your digestive system. Bile can no longer flow freely into the intestine, which can trigger a number of digestive problems.
A bile duct obstruction can be caused by several factors, including:
- Gallstones – These hardened deposits form in the gallbladder and can sometimes move into and block the bile duct.
- Tumours – Growths in or near the bile duct, liver, pancreas, or gallbladder can obstruct bile flow.
- Inflammation or scarring – Infections or conditions like pancreatitis can cause the bile duct to narrow or scar, restricting bile flow.
- Biliary strictures – Sometimes, following surgery or injury, the bile duct can narrow due to scar tissue, leading to obstruction.
Digestive Symptoms of a Bile Duct Obstruction
Because the bile duct plays such an important role in digestion, a blockage can result in noticeable and uncomfortable symptoms. Some of the most common digestive problems associated with bile duct obstruction include:
1. Jaundice (Yellowing of the skin and eyes)
One of the most tell-tale signs of a blocked bile duct is jaundice. When bile can’t reach the intestine, it backs up into the liver and spills into the bloodstream, causing a buildup of bilirubin (a yellowish pigment). This buildup leads to the yellowing of the skin and eyes which we call jaundice.
Aside from its visual symptoms, jaundice can also cause itching, dark-coloured urine, and light or clay-coloured stools. If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to consult a doctor, as jaundice is often a key indicator of bile duct obstruction or other liver-related issues.
2. Greasy, foul-smelling stools
Another digestive symptom you might experience with a bile duct obstruction is greasy or oily stools. This happens because bile helps digest fats, and when bile isn’t making its way into your intestines, fat from your food doesn’t get broken down properly.
The result is fatty stools (called steatorrhea), which can appear pale, greasy, and may float in the toilet. They often have a particularly foul smell. Over time, this can lead to weight loss and vitamin deficiencies, as your body isn’t absorbing fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) effectively.
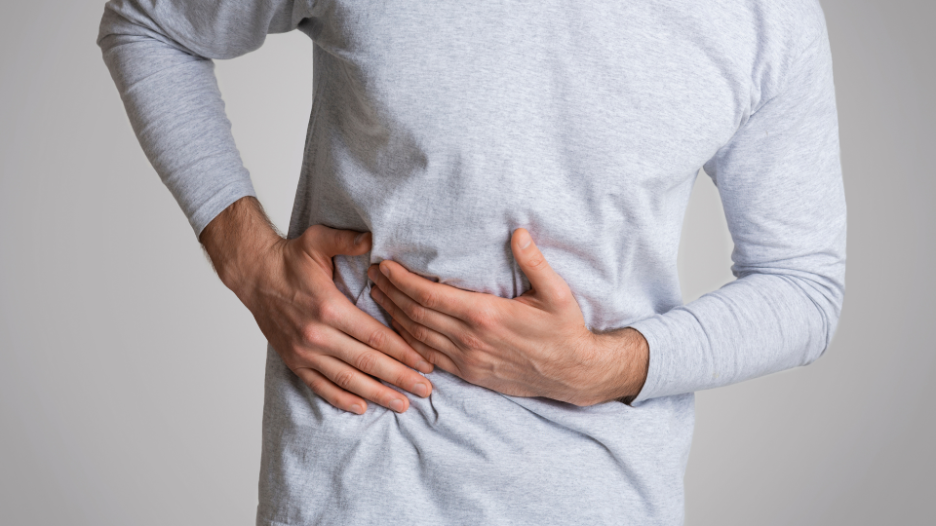
3. Abdominal pain and discomfort
Blocked bile ducts can also cause abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right side of your abdomen, under the rib cage. This pain can vary from mild discomfort to sharp, severe pain and may radiate to your back or shoulder. The pain is often worse after eating a fatty meal, as your digestive system is working harder to break down fat without sufficient bile.
Along with pain, you may also feel bloated or nauseous. Some people experience a loss of appetite or feel full after eating only a small amount of food.
Why You Shouldn’t Ignore These Symptoms
While a blocked bile duct may seem like a minor issue at first, it’s essential not to ignore these symptoms. If left untreated, bile duct obstructions can lead to more serious health problems, including:
- Cholangitis – This is a serious infection of the bile duct that can occur if bile remains backed up. It can cause fever, chills, and even life-threatening complications if not treated promptly.
- Liver damage – Ongoing bile duct obstruction can lead to liver inflammation and scarring, known as cirrhosis. Over time, this can affect your liver’s ability to function properly.
- Pancreatitis – Sometimes, bile duct obstructions can lead to inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), which causes severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Given these risks, it’s important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a bile duct obstruction. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent long-term damage and complications.
How Is Bile Duct Obstruction Diagnosed and Treated?
If your doctor suspects a bile duct obstruction, they will likely recommend tests like blood work, ultrasound, or imaging scans such as an MRI or CT scan to get a closer look at your bile duct.
Once diagnosed, treatment will depend on the cause of the obstruction. Some common treatments include:
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) – This minimally invasive procedure uses a flexible tube with a camera to locate and remove blockages in the bile duct, such as gallstones.
- Surgery – In cases where a tumour or severe scarring is causing the blockage, surgery may be required to remove the obstruction.
- Medication – In cases of infection or inflammation, antibiotics or other medications may be prescribed to reduce symptoms.
Don’t Wait to Get Checked
Digestive issues like jaundice, greasy stools, and abdominal pain can be uncomfortable, but they can also be warning signs of something more serious, like a bile duct obstruction. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, don’t ignore them. Seek medical advice and if necessary, treatment to protect your digestive and overall health.
Early detection and intervention can make a significant difference, preventing more serious complications down the road and helping you get back to feeling your best.