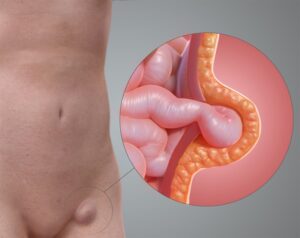
What is Appendicitis?
Appendicitis is a condition characterised by inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch in the lower right abdomen. The exact cause of appendicitis is not always clear. Still, it often occurs when the appendix becomes blocked by stool, a foreign body, or an infection, leading to bacterial overgrowth and inflammation.
Common Symptoms of Appendicitis
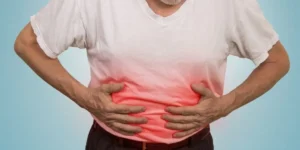
The hallmark symptom of appendicitis is abdominal pain, which typically starts around the belly button and then migrates to the lower right abdomen. Other common symptoms include:
- Nausea and Vomiting – Feeling sick to your stomach and vomiting.
- Loss of Appetite – Decreased desire to eat due to abdominal discomfort.
- Fever – Elevated body temperature, often indicating an infection.
- Tenderness – Pain or tenderness in the lower right abdomen, especially when pressing on the area.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Appendicitis is considered a medical emergency, and prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications such as a ruptured appendix. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Intense, persistent pain in the lower right abdomen.
- High fever accompanied by chills or shaking.
- Inability to keep food or liquids down.
- Difficulty passing gas or having a bowel movement.
Diagnosing Appendicitis
Your doctor will conduct a thorough evaluation to diagnose appendicitis, which may include:
- Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any recent changes in diet or lifestyle.
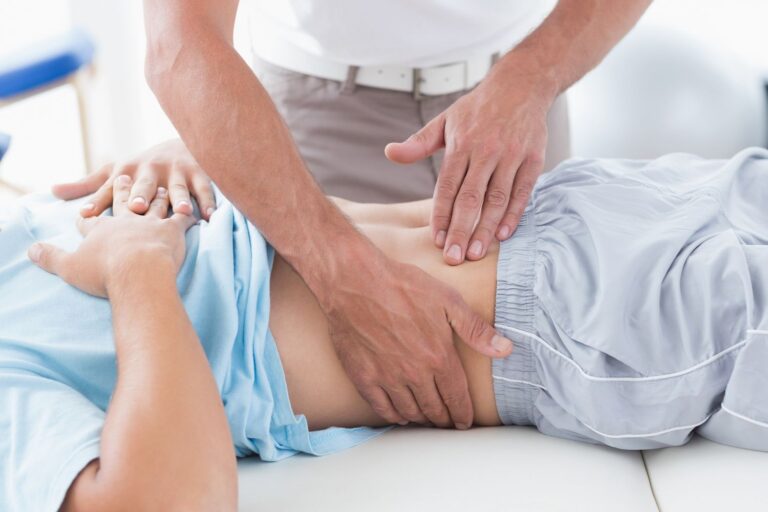
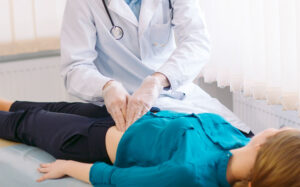
- Your abdomen will be examined for tenderness, swelling, or signs of peritonitis (inflammation of the abdominal lining).
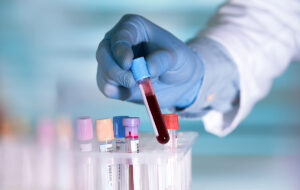
- Additional tests, such as blood tests, imaging studies (ultrasound, CT scan), or a urine test to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, may be ordered.
Treatment Options for Appendicitis
Treatment for appendicitis depends on the severity of the condition and whether the appendix has ruptured.
Antibiotics
In uncomplicated appendicitis, where the appendix has not ruptured, treatment may involve antibiotics to reduce inflammation and infection in the appendix. Antibiotics are typically administered intravenously in the hospital and may be followed by oral antibiotics to complete the treatment course at home. Antibiotic therapy can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications, but it may not always be effective in treating appendicitis, especially if the appendix has already ruptured.
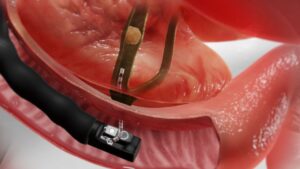
Appendicectomy
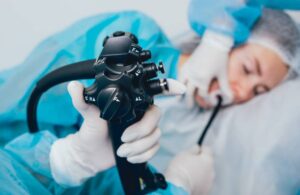
The standard treatment for appendicitis is surgical removal of the appendix, a procedure known as an appendectomy. This can be done through traditional open surgery or laparoscopic surgery, which involves smaller incisions and a faster recovery time. During the procedure, the surgeon removes the inflamed or ruptured appendix to prevent further complications such as peritonitis (inflammation of the abdominal lining). Appendicectomy is considered a curative treatment for appendicitis and is usually recommended to prevent recurrence of the condition.
Pain Management
Pain management is an essential aspect of treatment for appendicitis, as the condition can cause significant discomfort. Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioid analgesics, may be recommended to alleviate pain and improve the patient’s comfort level. Pain management strategies may also include using heat or ice packs to reduce inflammation and soothe abdominal pain.
Intravenous Fluids
In cases of severe appendicitis or complications such as dehydration, intravenous fluids may be administered to maintain hydration and electrolyte balance. This is typically done in the hospital setting, where the patient can be closely monitored for any changes in their condition. Intravenous fluids help prevent dehydration and support the body’s healing process during treatment for appendicitis.
Recovery and Prognosis
Most people recover well from appendicitis after undergoing surgery or receiving antibiotic treatment. After surgery, you may need to stay in the hospital for a day or two for observation and pain management. Recovery time varies, but most people can return to their normal activities within a few weeks. Following your doctor’s instructions for post-operative care and attending any follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery is essential.
If you have any concerns or questions about appendicitis or digestive health, don’t hesitate to reach out to our clinic Your proactive involvement in your healthcare journey can help ensure the best possible outcomes and a speedy recovery from appendicitis.