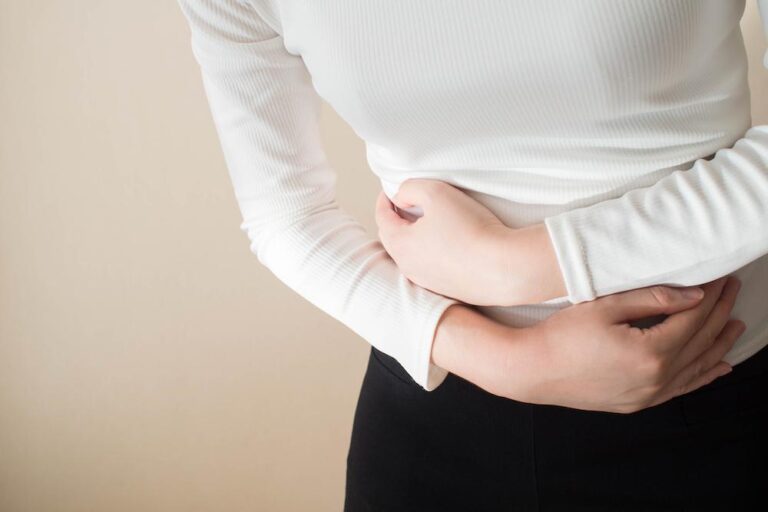
What is Abdominal Pain?
Abdominal pain refers to discomfort or pain felt in the area between the chest and the pelvis. This pain can range from mild to severe and may occur suddenly or develop gradually over time. Abdominal pain can be caused by a wide range of factors, including digestive issues, infections, inflammation, or underlying medical conditions.
Common Causes of Abdominal Pain
- Gastrointestinal Issues – Digestive disorders such as gastritis, gastroenteritis, acid reflux, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can cause abdominal pain.
- Gallbladder and Liver Conditions – Conditions affecting the gallbladder, such as gallstones or cholecystitis, as well as liver diseases like hepatitis or liver cirrhosis, can lead to abdominal pain.
- Pancreatic Disorders – Pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, or pancreatic cysts can cause abdominal pain, often accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or jaundice.
- Urinary Tract Issues – Kidney stones, urinary tract infections (UTIs), or bladder infections can manifest with abdominal pain, typically in the lower abdomen or back.
- Reproductive System Problems – Conditions affecting the reproductive organs, such as ovarian cysts, endometriosis, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), may cause abdominal pain, particularly in women.
Symptoms Associated with Abdominal Pain
In addition to pain, abdominal discomfort may be accompanied by other symptoms, including:
- Nausea and Vomiting – Feeling sick to your stomach or vomiting.
- Bloating – Sensation of fullness or bloating in the abdomen.
- Changes in Bowel Habits – Diarrhea, constipation, or changes in stool consistency.
- Fever – Elevated body temperature, which may indicate an infection or inflammation.
- Blood in Stool or Urine – The presence of blood in stool or urine requires prompt medical attention.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While mild abdominal pain may resolve on its own or with home remedies, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. These include:
- Intense or prolonged abdominal pain that does not improve with rest or over-the-counter medications.
- High fever accompanied by chills or shaking.
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing along with abdominal pain.
- The presence of blood in stool or vomit may indicate a serious medical condition.
- Recent injury or trauma to the abdomen, such as a fall or impact.
Diagnosing and Treating Abdominal Pain
If you experience abdominal pain, your doctor will conduct a thorough evaluation, which may include:
- Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any recent changes in diet or lifestyle.
- Your abdomen will be examined for tenderness, swelling, or other signs of underlying issues.
- Depending on your symptoms, your doctor may order diagnostic tests such as blood tests, imaging studies (ultrasound, CT scan), or endoscopic procedures (colonoscopy, upper endoscopy) to identify the cause of your abdominal pain.
Treatment for abdominal pain depends on the underlying cause and severity of the pain.
Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as paracetamol (Panadol) or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, ponstan, and voltaren may be recommended to alleviate mild to moderate abdominal pain. For specific conditions such as acid reflux or gastritis, medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or antacids may be prescribed to reduce stomach acid and relieve discomfort.
Dietary Changes
In cases where abdominal pain is related to digestive issues such as gastritis, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), dietary modifications may be beneficial. This could involve avoiding trigger foods such as spicy, fatty, or acidic foods and incorporating more fibre-rich foods, probiotics, and hydration to promote digestive health.
Lifestyle Changes
Certain lifestyle changes may help alleviate or prevent abdominal pain, such as stress management through relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. Regular exercise, adequate hydration, and a healthy weight can also support overall digestive health and reduce the risk of abdominal discomfort.
Medical Procedures
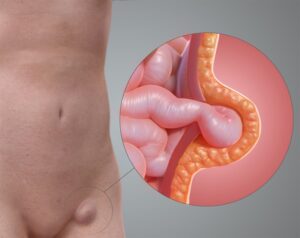
In some cases, medical procedures may be necessary to diagnose and treat the underlying cause of abdominal pain. This could include diagnostic tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or endoscopy to identify any structural abnormalities or inflammatory conditions in the abdomen. Depending on the findings, therapeutic procedures like endoscopic therapy to treat ulcers or gallstones or surgery to remove diseased organs or repair hernias may be recommended.
Pain Management
If abdominal pain is severe or persistent, prescription pain medications or muscle relaxants may be prescribed to provide relief. These medications should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional and for a limited duration to avoid dependence or other adverse effects.
Abdominal pain can be a distressing symptom with a wide range of potential causes. While occasional mild abdominal discomfort is common and often resolves on its own, persistent or severe abdominal pain requires medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment. If you experience abdominal pain along with concerning symptoms such as fever, vomiting blood, or difficulty breathing, seek immediate medical attention. Remember, early detection and treatment offer the best chance for successful outcomes in managing abdominal pain and related conditions.
Don’t hesitate to contact our clinic if you have any concerns or questions about abdominal pain or digestive health. Your proactive involvement in your healthcare journey can significantly impact your overall health and well-being.