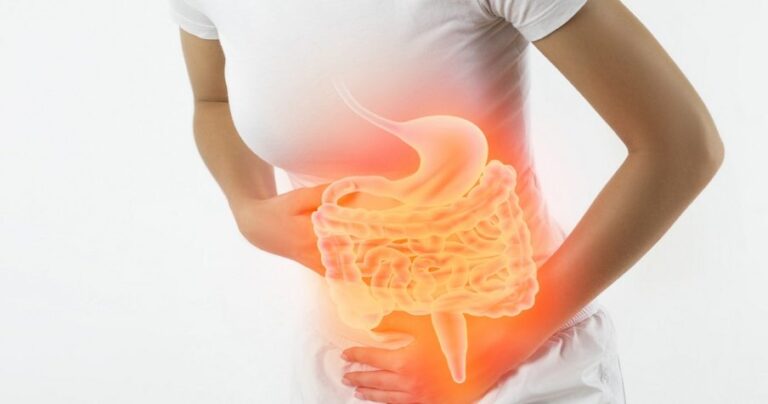
What are Upper Gastrointestinal Conditions?
Upper gastrointestinal conditions refer to disorders affecting the upper part of the digestive system, including the oesophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). These conditions can range from mild to severe and can significantly impact your overall health and quality of life.
Common Types of Upper GI Conditions
There are several common upper GI conditions, each with its unique characteristics and challenges:
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the oesophagus, causing irritation. Common symptoms include heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing.
Peptic Ulcer Disease
Peptic ulcers are open sores that develop on the inner lining of the stomach, upper small intestine, or oesophagus. They are often caused by infection with H. pylori bacteria or long-term use of NSAIDs.
Gastritis
Gastritis is the inflammation of the stomach lining, which can be acute or chronic. It may be caused by excessive alcohol use, chronic vomiting, stress, or certain medications.
Esophagitis
Esophagitis is inflammation of the oesophagus, often resulting from acid reflux, infections, or allergies. Symptoms include difficulty swallowing, chest pain, and heartburn.
Barrett's Esophagus
A condition in which the tissue lining the oesophagus changes due to chronic acid exposure from GERD. It can increase the risk of developing oesophagal cancer.
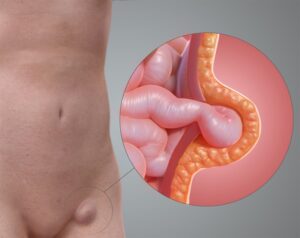
Hiatal Hernia
A condition where part of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, often causing reflux symptoms and discomfort.
Celiac Disease
An autoimmune disorder where ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine, causing various digestive and systemic symptoms.
Esophageal Cancer
A type of cancer that occurs in the esophagus often linked to smoking, heavy alcohol use, and chronic acid reflux.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors for upper GI conditions can help in prevention and management:
- Dietary habits, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and stress can contribute to the development of upper GI conditions.
- Infections such as H. pylori can lead to peptic ulcers and gastritis.
- Long-term use of NSAIDs, steroids, and certain other medications can cause or exacerbate upper GI conditions.
- A family history of certain upper GI conditions, such as celiac disease, can increase your risk.
- Conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and connective tissue disorders can contribute to the development of upper GI conditions.
Symptoms
Symptoms of upper GI conditions can vary widely depending on the specific disorder but may include:
- A burning sensation in the chest, often after eating, which may be worse at night.
- A sour or bitter-tasting acid backing up into your throat or mouth.
- Pain or discomfort when swallowing, which can be caused by inflammation or narrowing of the oesophagus.
- Pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen, which may be related to ulcers, gastritis, or other conditions.
- Feeling sick to your stomach or vomiting, which can be a sign of various upper GI disorders.
- Feeling bloated or having excessive gas, which can be associated with conditions like gastritis or celiac disease.
- Unintentional weight loss can be a symptom of serious upper GI conditions, such as cancer or severe peptic ulcer disease.
Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of upper GI conditions is essential for effective treatment. Common diagnostic procedures include:
Endoscopy
A procedure where a flexible tube with a camera is inserted down the throat to view the oesophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
Biopsy
A small tissue sample may be taken during an endoscopy to check for infections, cancer, or other abnormalities.
Imaging Tests
X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans can help visualize the upper GI tract and identify structural abnormalities.
pH Monitoring
A test that measures the acidity in the oesophagus to diagnose GERD.
Blood Tests
Used to detect infections like H. pylori, celiac disease antibodies, and other markers of disease.
Stool Tests
Used to check for the presence of H. pylori, occult blood, and other indicators of GI conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for upper GI conditions varies depending on the specific disorder and its severity. Common treatment options include:
- Antacids – Provide quick relief by neutralising stomach acid.
- H2 Receptor Blockers – Reduce acid production.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) – Significantly reduce stomach acid production.
- Antibiotics – Used to treat H. pylori infections.
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs – Treat inflammation associated with conditions like esophagitis.
- Diet – Avoid trigger foods and eat smaller, more frequent meals.
- Weight Management – Losing weight can help reduce symptoms of GERD and other conditions.
- Avoiding Tobacco and Alcohol – Reduces irritation of the GI tract.
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary:
- Fundoplication – A procedure to reinforce the lower esophageal sphincter, often used for GERD.
- Gastrectomy – Removal of part or all of the stomach, used for severe ulcers or cancer.
- Esophagectomy – Removal of part or all of the oesophagus, used for oesophagal cancer.
- Alternative Therapies – Some patients find relief through complementary treatments such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, and relaxation techniques.
Managing and Preventing Upper GI Conditions
Effective management and prevention strategies can help minimise symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Regular visits to your healthcare provider can help monitor your condition and catch any changes early.
- Adopting a balanced diet that avoids known triggers can prevent flare-ups.
- Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress, which can exacerbate GI symptoms.
- If possible, use alternatives to NSAIDs to avoid irritating the GI tract.
- Adhering to prescribed medications and treatment regimens can effectively manage symptoms and prevent complications.