Key Pointers
- Dyspepsia refers to persistent discomfort or fullness in the upper abdomen.
- Common symptoms include bloating, burping, nausea, and upper stomach pain.
- It can be caused by acid reflux, gastritis, or Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection.
- Lifestyle factors such as eating too quickly or consuming fatty foods can worsen symptoms.
- Persistent bloating or discomfort should be evaluated by a gastro specialist.
What Is Dyspepsia?
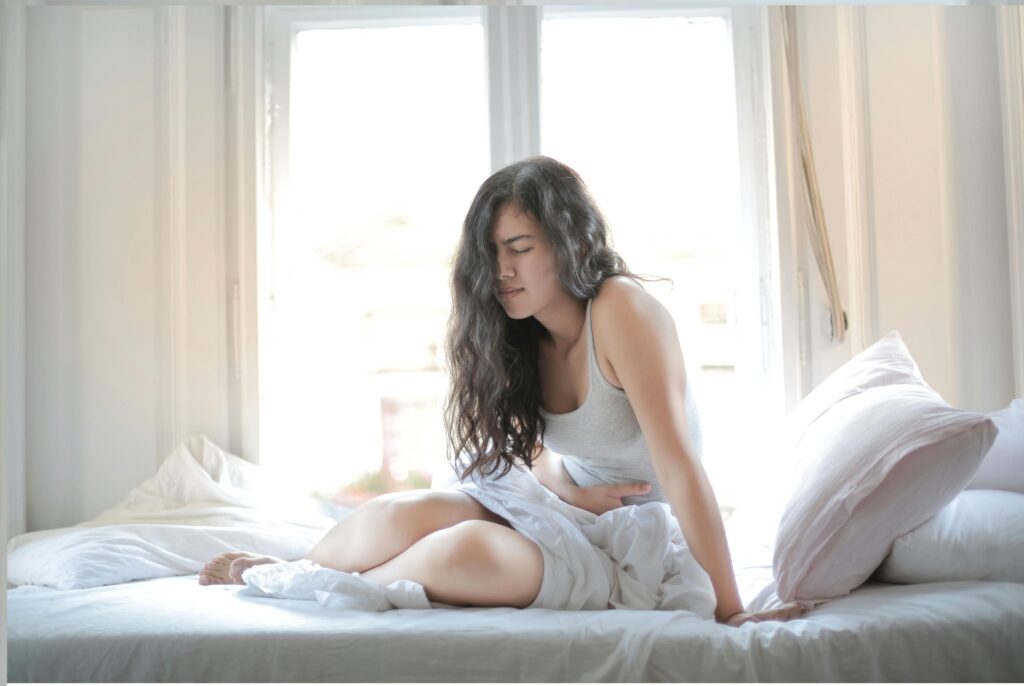
Dyspepsia, also known as indigestion, describes a group of symptoms related to discomfort in the upper abdomen. People with dyspepsia often report feeling full quickly during meals, bloated afterward, or experiencing mild pain or burning in the stomach area.
Occasional indigestion is common, but when these sensations happen often or last for weeks, it may indicate an underlying digestive issue that needs attention.
Why Do I Feel Bloated or Full All the Time?
Bloating and fullness may result from several factors. Some of the most common include:
- Overeating or eating too quickly – Swallowing excess air can lead to trapped gas.
- High-fat or spicy foods – These delay stomach emptying and can cause discomfort.
- Acid reflux (GERD) – When stomach acid flows upward, it can irritate the oesophagus and cause fullness or burning.
- Gastritis or stomach inflammation – Often linked to infection by H. pylori.
- Stress and irregular meals – Emotional tension or skipped meals can alter digestion.
Understanding your eating habits and triggers can help you determine whether your bloating is occasional or persistent.
How Is Dyspepsia Different from Bloating?
While bloating refers to a feeling of tightness or swelling in the abdomen, dyspepsia includes a wider set of symptoms that often occur together. These may include:
- Early satiety (feeling full too soon)
- Upper abdominal discomfort
- Belching or gas
- Nausea after meals
- Burning in the upper abdomen
If you experience several of these symptoms frequently, it may be more than simple bloating, it could be dyspepsia.
When Should I See a Doctor About Persistent Fullness?
You should seek medical attention if you notice any of the following:
- Constant bloating or discomfort that lasts more than two weeks
- Unexplained weight loss or fatigue
- Vomiting, loss of appetite, or dark stools
- Difficulty swallowing or persistent nausea
These could point to conditions such as peptic ulcer disease, acid reflux (GERD), or H. pylori infection, all of which benefit from proper diagnosis and treatment.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Dyspepsia?
During a consultation, your doctor will review your symptoms, diet, and medical history. Depending on your condition, you may be recommended tests such as:
- Gastroscopy (Upper Endoscopy): to visually inspect the stomach and oesophagus for inflammation or ulcers.
- H. pylori Testing: to detect infection that may cause chronic gastritis or ulcers.
- Ultrasound or Blood Tests: to rule out other abdominal issues.
These investigations help identify the cause of symptoms and guide an appropriate management plan.
How Can I Relieve Dyspepsia Symptoms at Home?
While professional evaluation is important for ongoing symptoms, you can make small changes to ease mild discomfort:
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals.
- Avoid lying down immediately after eating.
- Limit coffee, alcohol, and spicy foods.
- Manage stress and maintain regular meal times.
- Stay upright for at least an hour after meals.
These simple habits can help improve digestion and reduce symptoms of fullness and bloating.
FAQs About Dyspepsia
1. What does dyspepsia feel like? Dyspepsia often feels like upper abdominal discomfort, bloating, or a burning sensation after meals.
2. Can stress cause dyspepsia? Yes. Stress can alter digestion, increase acid production, and worsen symptoms like bloating or nausea.
3. What foods make indigestion worse? Fried, fatty, spicy, or acidic foods, as well as caffeine and alcohol, commonly trigger dyspepsia.
4. Is dyspepsia the same as acid reflux? They can overlap. Dyspepsia describes general upper abdominal discomfort, while reflux involves acid moving up into the oesophagus.
5. How is dyspepsia treated? Treatment depends on the cause. Doctors may prescribe acid-reducing medication, antibiotics for H. pylori infection, or lifestyle modifications.
When Bloating Becomes a Signal to Act
Constant fullness or bloating isn’t always harmless. Persistent symptoms may indicate something deeper, such as reflux, gastritis, or H. pylori infection, that can be identified and treated effectively once properly evaluated.
Take Control of Your Digestive Health
At the Clinic for Digestive Surgery, patients can receive evaluation and management for dyspepsia, reflux, and related gastrointestinal concerns. Diagnostic tests such as gastroscopy may be recommended to confirm the cause and guide a treatment plan.
📍 Locations:
- Mount Elizabeth Novena Specialist Centre
- Mount Alvernia Hospital
📞 Contact: +65 6570 2702 | [email protected]
👉 Feeling Bloated Too Often? It Might Be Time to Get Checked.
Book a Consultation with our doctors to understand your symptoms and support your digestive wellness.