What are Gallbladder Infections?
Gallbladder infections, or cholecystitis, occur when the gallbladder becomes inflamed due to bacterial infection or obstruction of the bile ducts. The gallbladder is a small organ located beneath the liver. Its primary function is to store bile produced by the liver and release it into the small intestine to aid in digestion. When the flow of bile is disrupted, either by infection or obstruction, it can lead to inflammation and infection of the gallbladder.
Common Causes of Gallbladder Infections
Several factors can contribute to the development of gallbladder infections, including:
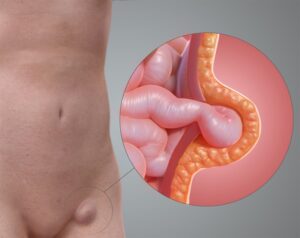
- Gallstones – The most common cause of gallbladder infections is the presence of gallstones, which can block the flow of bile and lead to inflammation.
- Biliary Sludge – Thickened bile or biliary sludge can also obstruct the bile ducts and increase the risk of infection.
- Bacterial Infection – In some cases, gallbladder infections may be caused by bacterial infection, particularly in individuals with a weakened immune system or a history of recurrent infections.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Infections
The symptoms of gallbladder infections can vary in severity but often include:
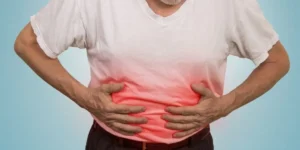
- Abdominal Pain – Pain in the upper right abdomen that may radiate to the back or shoulder blades.
- Fever and Chills – Elevated body temperature and chills, indicating an inflammatory response.
- Nausea and Vomiting – Feeling sick to your stomach and vomiting.
- Jaundice – Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to bile duct obstruction.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Gallbladder infections can be serious and require prompt medical attention. Seek medical care if you experience:
- Intense, persistent pain in the upper right abdomen.
- High fever accompanied by chills or shaking.
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Inability to keep food or liquids down.
Diagnosing Gallbladder Infections
To diagnose a gallbladder infection, your doctor will perform a thorough evaluation, which may include:
- Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any risk factors for gallbladder disease.
- Your abdomen will be examined for tenderness, swelling, or signs of infection.
- Additional tests may be ordered, such as blood tests, ultrasound, or a CT scan, to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the infection.
Treatment Options for Gallbladder Infections
Treatment for gallbladder infections depends on the severity of the infection and underlying causes. Options may include:
Antibiotics
This treatment option involves the use of antibiotics to target and eliminate the bacterial infection causing the gallbladder infection. Antibiotics are typically prescribed for mild infections and work by killing the bacteria responsible for the infection. They also help reduce inflammation in the gallbladder, aiding in the healing process and preventing the infection from spreading.
Pain Management
Pain management is an essential aspect of treatment for gallbladder infections, as the condition can cause significant discomfort. Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioid analgesics, may be recommended to alleviate pain and improve the patient’s quality of life. Pain management strategies may also include lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes to avoid triggering pain or discomfort.
Surgery
In cases of severe or recurrent gallbladder infections that do not respond to antibiotics or conservative management, surgical removal of the gallbladder, known as cholecystectomy, may be necessary. This procedure is typically performed laparoscopically, using small incisions and specialised instruments to remove the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is considered a definitive treatment for gallbladder infections and can help prevent future episodes of infection or complications such as gallstones or bile duct obstruction.
Recovery and Prognosis
Most people recover well from gallbladder infections with appropriate treatment. After surgery or antibiotic therapy, you may need to follow dietary recommendations and temporarily avoid fatty or greasy foods. Recovery time varies, but most people can return to normal activities within a few weeks. Following your doctor’s instructions for post-treatment care and attending any follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery is essential.
Gallbladder infections can be painful and debilitating, but with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, most people can recover well. If you experience symptoms of a gallbladder infection, such as abdominal pain, fever, nausea, or jaundice, seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention offers the best chance for successful outcomes and reduces the risk of complications. Remember, your health is important, and proactive management of gallbladder infections can help ensure the best possible outcomes and a speedy recovery.
Don’t hesitate to contact our clinic with any concerns or questions about gallbladder infections or digestive health. Your proactive involvement in your healthcare journey can significantly impact your overall well-being.