What are Hepatobiliary Conditions?
Hepatobiliary conditions refer to disorders affecting the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and bile. These conditions can range from mild to severe and can significantly impact your overall health and quality of life. The liver and biliary system play crucial roles in digestion, detoxification, and metabolism, making their proper function essential for health.
Common Types of Hepatobiliary Conditions
There are several common hepatobiliary conditions, each with its unique characteristics and challenges:
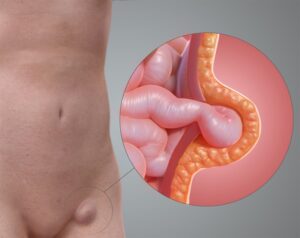
Gallstones
Solid particles that form in the gallbladder from bile cholesterol and bilirubin. They can cause pain, infection, and blockages in the bile ducts, leading to cholecystitis (gallbladder inflammation) or pancreatitis.
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder, often caused by gallstones blocking the bile ducts. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, fever, and nausea.
Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC)
A chronic disease in which the bile ducts in the liver are slowly destroyed. This can lead to bile buildup in the liver, causing inflammation and scarring. Symptoms include fatigue, itching, and jaundice.
Fatty Liver Disease
A condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. It can be non-alcoholic (NAFLD) or alcoholic (AFLD). Symptoms are often mild or absent but can include fatigue and abdominal discomfort.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors for hepatobiliary conditions can help in prevention and management:
- Excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, and lack of physical activity can contribute to liver disease and gallstones.
- Viral infections such as hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E are significant causes of liver inflammation and damage.
- Certain conditions, like biliary atresia and some forms of cirrhosis, have genetic components.
- Autoimmune hepatitis and primary biliary cholangitis are examples of the immune system attacking liver cells or bile ducts.
- Obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome increase the risk of fatty liver disease and gallstones.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hepatobiliary conditions can vary widely depending on the specific disorder but may include:
Jaundice
Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to elevated bilirubin levels, often indicating liver dysfunction.
Abdominal Pain
Pain or discomfort in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, which can be associated with liver inflammation, gallstones, or bile duct blockages.
Fatigue
Persistent tiredness and weakness, common in many liver and biliary conditions.
Nausea and Vomiting
Feeling sick to your stomach or vomiting, which can be a sign of various hepatobiliary disorders.
Itching
Chronic itching (pruritus) can occur due to bile buildup in the bloodstream.
Weight Loss
Unintentional weight loss can be a symptom of serious liver conditions, such as cancer or severe cirrhosis.
Dark Urine and Pale Stools
Changes in urine and stool colour can indicate bile flow issues.
Swelling
Swelling in the abdomen (ascites) or legs (oedema) due to liver dysfunction.
Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of hepatobiliary conditions is essential for effective treatment. Common diagnostic procedures include:
Blood Tests
Tests to assess liver function (liver enzymes, bilirubin levels), detect viral hepatitis, and measure other relevant markers.
Imaging Tests
Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI scans help visualise the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts, identifying structural abnormalities and blockages.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
A procedure that combines endoscopy and X-ray imaging to diagnose and treat bile duct problems.
Liver Biopsy
A small sample of liver tissue is taken for examination under a microscope to assess the extent of liver damage or identify specific conditions.
FibroScan
A non-invasive test that measures liver stiffness to assess fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for hepatobiliary conditions varies depending on the specific disorder and its severity. Common treatment options include:
- Antivirals – Used to treat chronic hepatitis B and C infections.
- Anti-inflammatories – To reduce liver inflammation.
- Bile Acids – For conditions like primary biliary cholangitis.
- Pain Relievers and Anti-nausea Drugs – To manage symptoms.
- Diet – A healthy diet can help manage liver conditions and prevent gallstones.
- Weight Management – Losing weight can help reduce fat in the liver and decrease the risk of gallstones.
- Avoiding Alcohol – Essential for preventing further liver damage in many conditions.
- Cholecystectomy – Removal of the gallbladder, commonly performed to treat gallstones or cholecystitis.
- Liver Transplant – For severe liver disease or liver cancer that cannot be managed by other treatments.
- Bile Duct Surgery – To remove blockages or repair bile ducts.
- ERCP – Used to remove bile duct stones, place stents, or perform biopsies.
- Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiography (PTC) – A procedure to visualise the bile ducts and treat obstructions.
- Alternative Therapies – Some patients find relief through complementary treatments such as herbal remedies, acupuncture, and lifestyle modifications.
Managing and Preventing Hepatobiliary Conditions
Effective management and prevention strategies can help minimise symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Regular visits to your healthcare provider can help monitor your condition and catch any changes early.
- Adopting a balanced diet that avoids known triggers can prevent flare-ups and manage symptoms.
- Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress, which can exacerbate GI symptoms.
- Vaccines for hepatitis A and B can prevent these viral infections.
- Reducing exposure to liver-damaging substances, such as alcohol and certain medications, is crucial.
- Adhering to prescribed medications and treatment regimens can effectively manage symptoms and prevent complications.