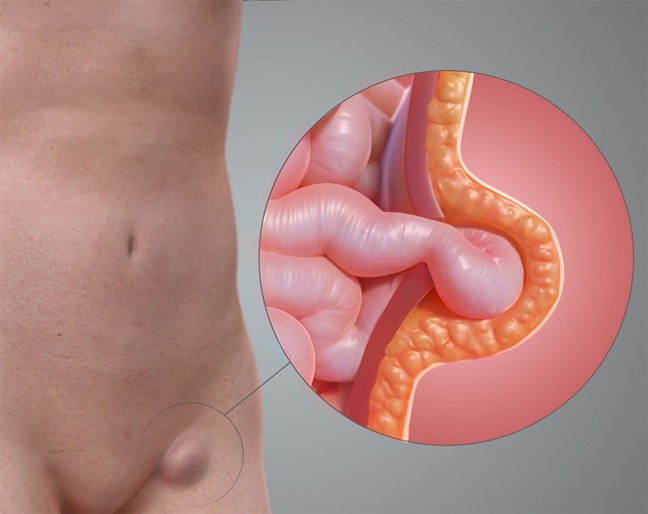
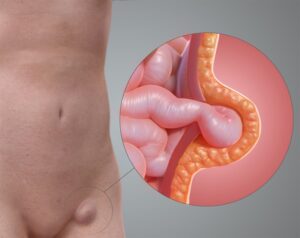
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. Painful hernias can cause significant discomfort and require prompt medical attention.
Common Types of Painful Hernias
Inguinal Hernia
Occurs in the groin area when part of the intestine protrudes through the abdominal wall. Common in men and can cause pain, especially when lifting, coughing, or bending.
Umbilical Hernia
Occurs near the belly button when part of the intestine protrudes through the abdominal wall. Common in infants but can also affect adults.
Hiatal Hernia
Occurs when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, causing heartburn, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing.
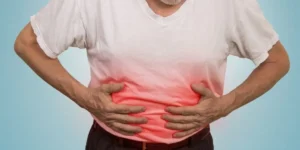
Symptoms of Painful Hernias
- Visible bulge or lump in the affected area
- Pain or discomfort, especially when bending, coughing, or lifting
- Nausea and vomiting (in severe cases)
- Difficulty swallowing (for hiatal hernias)
Diagnosis of Painful Hernias
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical Examination – Checking for visible bulges and tenderness.
- Imaging – Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI to confirm the hernia and assess its severity.
- Endoscopy – For hiatal hernias, to visualise the inside of the oesophagus and stomach.
Treatment Options for Painful Hernias
- Lifestyle Changes – Weight management and avoiding heavy lifting.
- Medications – For hiatal hernias, antacids and proton pump inhibitors to manage symptoms.
- Surgery – Hernia repair surgery to close the hole and reinforce the weakened area with mesh.